Management Tools
What is “Fish Bone Diagram” and how to implement it?
The beginning:
This method was developed by “Kaoru Ishikawa” who pioneered the quality management process in KAWASAKI shipyards and became one of the founding fathers of modern management. The basic concept was first used in 1920 and became popular in the 1960s.
Dr. Edwards Deming also adopted this technique. Both Ishikawa and Deming used this diagram as one of the first tools in the quality management approach. Dr. Deming has taught methods of quality management in Japan since WW2 to the Japanese army.
The rational of the technique:
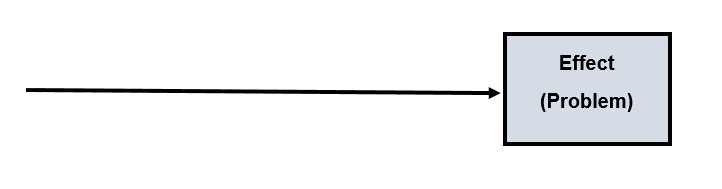
This technique’s philosophy is based on the (Effect) is the problem you are dealing with, however, there is a hidden cause you need to find in order to eliminate and solve the problem permanently.
This tool helps to identify the contributing factors to the problem. Therefore, further investigation can be conducted. It is commonly used for product design and quality defect prevention.
This method is also called the “Ishikawa diagram” or “fishbone diagram” because its shape looks like a side view of a fish skeleton.
How does it work?
The Fishbone diagram works with complex problems and gives a comprehensive vision of the whole process. In addition, it is considered a good tool to visualize the situation to stakeholders.
Fishbone diagram process:
- Assemble a team:
The problem-solving team should contain people who have hands-on experience and knowledge of the process. People who are close to the problem see more details than anybody else and are probably able to propose practical solutions.
- Identify the problem:
Identifying the problem is the most crucial step in any problem-solving technique. As it is the starting point of the whole process and the foundation that all efforts will be based on.
- Identify the possible casual factors:
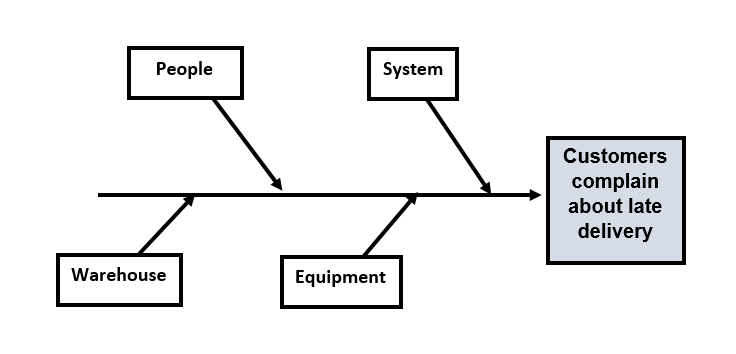
There are typical categories of each business or industry. These categories include all functions the business needs to run. They are the factors or causes of the problem. Each potential cause is traced back to find the root cause, often using the (five Whys, appreciation, and drill down) techniques.
Typical categories include:
Originating with lean manufacturing and the Toyota Production System, the 5 Ms is one of the most common frameworks for root-cause analysis: [1]
The 5 Ms (used in manufacturing)
- Man / mind power (physical or knowledge work, includes suggestions)
- Machine (equipment, technology)
- Material (includes raw material, consumables, and information)
- Method (process)
- Measurement / medium (inspection, environment)
These have been expanded by some to include an additional three, and are referred to as the 8 Ms: [2]
- Mission / mother nature (purpose, environment)
- Management / money power (leadership)
- Maintenance
The 8 Ps (used in product marketing)
This common model for identifying crucial attributes for planning in product marketing is often also used in the root-cause analysis as categories for the Ishikawa diagram: [3]
- Product (or service)
- Price
- Place
- Promotion
- People (personnel)
- Process
- Physical evidence
- Performance
The 8 Ps are primarily used in product marketing.
The 4 Ss’ (used in service industries)
An alternative used for service industries uses four categories of possible causes : [4]
- Surroundings
- Suppliers
- Systems
- Skill
- Write down the problem (the effect) on the side of a paper or board.
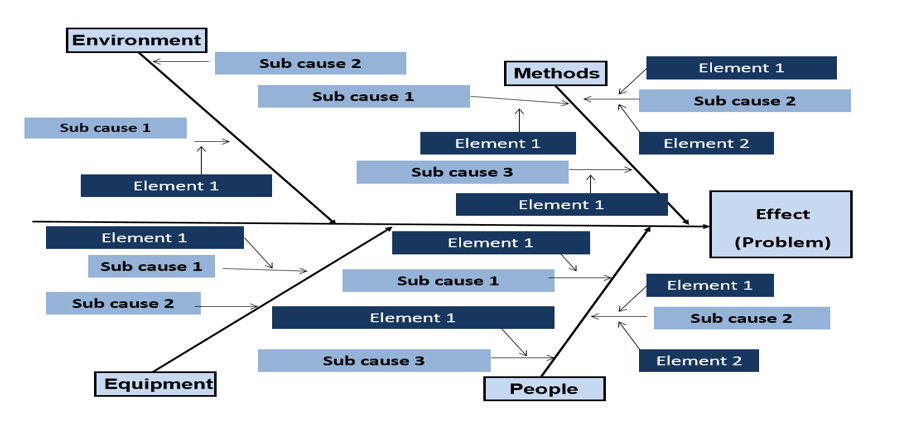
- Identify the relevant category according to the type of business (you may refer to the typical categories in step two or manage your categories according to your process). Then draw the branches off the main one. Each category is a potential cause where you can find the defect in.

- Brainstorm every cause to identify the sub causes, and then draw branches off every category to write down the sub causes you identified.

- Break down each sub cause into its elements. Then Draw your lines off the sub causes you determined in the previous step.
- Analyze your diagram by asking the following questions:
How likely is this cause to be the major source of the issue or variation?
- V – Very Likely
- S – Somewhat Likely
- N – Not Likely
How easy would it be to fix or control?
- V – Very Easy
- S – Somewhat Easy
- N – Not Easy
Put the answers to the two questions together. Work on the Causes that have a result of VV, VS, and SV. [5]
Example:
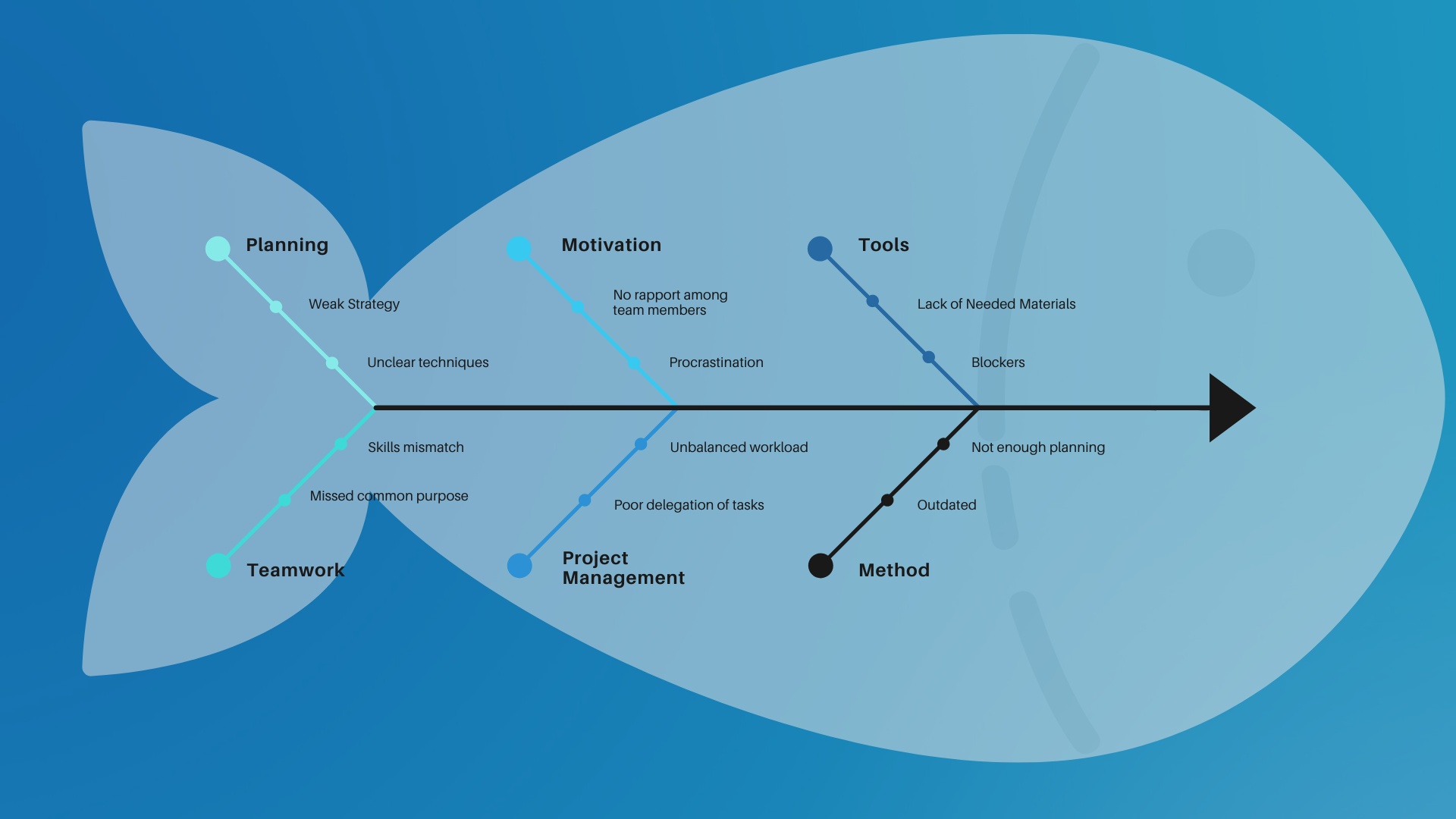
Using this method will illustrate the complexity of a “late delivery” problem.
The problem-solving team identified the problem by observing the frequent complaints about late delivery. Then collected data about the whole delivery process and all tasks that needed to be done to make the delivery on the expected time and decided to analyze it by a “fishbone” diagram according to the complexity of the problem.

Step two: Determining the possible casual factors by including all categories, which can be the causes of the problem.
Step three: Brainstorm each cause and find the sub causes:
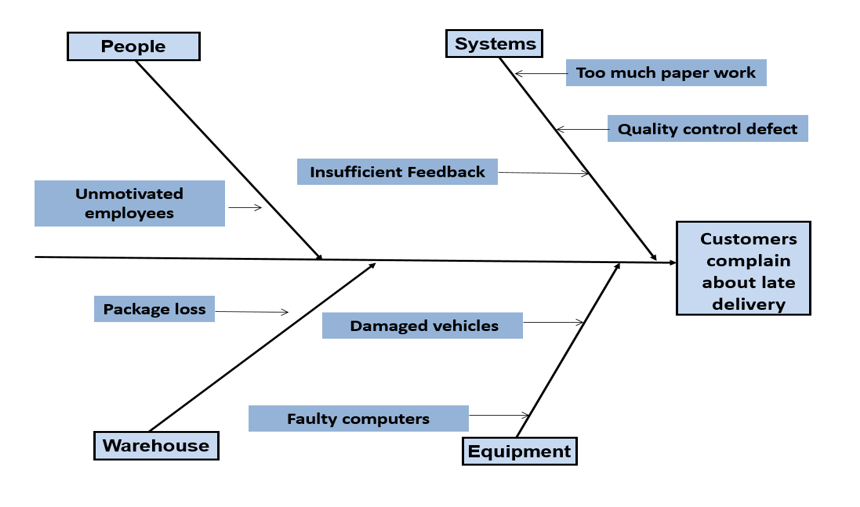
Step four: Break down each sub-cause into its elements. Then Draw your lines off the sub causes you determined in the previous step.
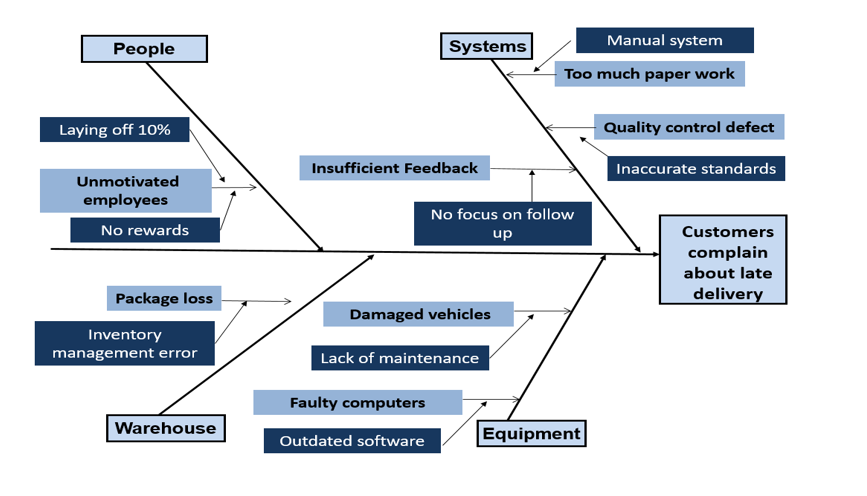
Step five: Analyze your diagram by asking the following questions:
- How likely is this cause to be the major source of the issue or variation?
- How easy would it be to fix or control?
Step Six: Determine the root cause(s) of the problem.
Step seven: you may use one of the other problem-solving techniques (5whys, appreciation, and drill down) to analyze each element for more details if needed.
[1] Weeden, Marcia M. (1952). Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEAs) for small business owners and non-engineers: determining and preventing what can go wrong. ISBN 0873899180. OCLC 921141300.
[2] Bradley, Edgar (2016-11-03). Reliability engineering: a life cycle approach. ISBN 978-1498765374. OCLC 963184495.
[3] Bradley, Edgar (2016-11-03). Reliability engineering: a life cycle approach. ISBN 978-1498765374. OCLC 963184495.
[4] Dudbridge, Michael (2011). Handbook of Lean Manufacturing in the Food Industry. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1444393118. OCLC 904826764.
[5] “Fishbone Diagram – How to Make and Use a Fishbone Diagram”. www.lbspartners.ie. LBSPartners. Retrieved 17 August 2017.
Management Tools
The Ultimate Time Management System for Busy People
Manage your time effectively with this step-by-step system. Learn how to manage your time more efficiently so you can accomplish what matters most.
Time management is an important skill for anyone who wants to succeed in life. This article will teach you how to use time wisely and effectively.

Set Goals.
If you want to become successful at anything, you need to set goals. You also need to make lists and prioritize tasks. These three steps are essential to managing your time well.
To be a better manager of time is setting goals. You should set goals for yourself every day. If you want to be successful at something, you must know what you want to accomplish. When you set goals, you are able to focus on one thing at a time. For example, if you want to lose weight, then you should set a goal to eat less than 1,500 calories per day. By focusing on one goal at a time, you will be able to achieve success.
Prioritize Tasks.
The first step to becoming a better time manager is to prioritize tasks. You should always be working towards accomplishing one task at a time. If you try to accomplish too many things at once, you won’t get anything done. When you work on multiple projects simultaneously, you end up spending less time on each project than if you had focused on one thing at a time.
To start, you should identify your top priorities. Then, make a list of everything else you need to do. Finally, set realistic deadlines for each task. This will help you stay focused and avoid procrastination.
Break Down Big Projects into Smaller Steps.
If you have a big project to complete, break it down into smaller steps. You can use a calendar to keep track of when tasks must be completed. Also, try to work on one thing at a time. It will help you focus on one goal instead of getting distracted by other things.
For example, if you want to write a book, you should first decide what chapters you want to include. Once you know which chapters you want to include, you can then determine how many pages each chapter will contain. You can then divide those pages into sections, and finally, you can create a table of contents. By breaking down your project into smaller steps, you will be able to accomplish much more than if you had simply started writing without planning ahead.
Plan Ahead.
To make sure you stay organized, plan out your day and week ahead of time. This helps you avoid procrastination because you know exactly what needs to be done.
You should plan ahead and set goals for yourself. When you know what you want to accomplish, you can better organize your day and get things done efficiently.
If you know what you want to accomplish during a certain period of time, then you can better manage your time. For example, if you plan to study for an exam, you should set aside enough time to complete the task. You should also be aware of the amount of time required to complete each assignment.
*Learn: How to manage Unplanned and Sudden Tasks in 6 Steps like a Master? – SKILLTECS
*Also learn more about planning here: All You Need to Know About Planning – YouTube
Create a To Do List.
Start by creating a list of everything you need to do today. Then prioritize each task based on its importance and urgency. If something isn’t urgent, put it off until later.
The most important step to creating a productive schedule is to create a to-do list. A to-do list helps you stay organized and focused on what needs to be done. You should write down everything that you want to accomplish during the day.
If you find yourself procrastinating, then you might want to add some tasks to your list. For example, if you know that you tend to put off cleaning until the last minute, then you could add cleaning to your list. Once you have created your list, try to stick to it. Don’t let other things distract you from accomplishing your goals.
Business
5 Quality Management Principles Every Manager Must Understand

Quality management is an approach that helps companies improve the products and services they offer. It focuses on improving processes, procedures, and systems in order to ensure that customers receive high-quality products and services.
However, Quality control is one of the most important aspects of business. If you want to be successful, you must focus on quality. You should always strive to provide the best product possible. Here are
The Five Ws of Quality Management
There are five key elements of quality management: what, who, when, where, and why. These five elements help define the quality of a company’s products and services.
What: What does the company produce? This includes its products and services.
Who: Who is responsible for producing the product or providing the service?
When: When do they need to deliver the product or provide the service?
Where: Where will the product or service be delivered?
Why: Why should people buy the product or use the service?
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is an approach to improving business processes by using statistical methods. It focuses on eliminating defects and reducing variation in production.
The goal of quality management is to eliminate defects from the manufacturing process. Defects occur when there is something wrong with the product or service.
For example, if a customer receives a defective car, then the manufacturer has failed to meet the customer’s expectations. In contrast, a defect-free car would be one where the customer received what he or she expected.
The Deming Cycle
Deming was one of the first people to apply the scientific method to manufacturing. He developed the concept of “quality circles” as a means of improving quality through teamwork. His work led to the development of the six-sigma process improvement methodology. It’s also known as Deming wheel or PDCA which stands for: Plan, Do, Check, and Act.
The Five S’s of Quality Management
The five s’s of quality management are:
1) Standardize – Make sure everything is consistent across your organization.
2) Simplify – Eliminate unnecessary steps and processes.
3) Speed up – Reduce the number of steps required to complete tasks.
4) Systematize – Create an organized system for managing your business.
5) Share knowledge – Provide training to employees so everyone knows how to do their jobs correctly.
The Six Ps of Quality Control
These six principles are used by companies to ensure that products meet customer expectations. They also help to improve the efficiency of operations and reduce costs.
These six Ps include planning, production, packaging, promotion, pricing, and post-sale service.
Planning is essential because if you don’t plan, then you won’t know what needs to be done. Without planning, you won’t know where to start. When you plan, you set goals and objectives. These goals help you determine what you want to accomplish. Once you’ve determined what you want to accomplish, you can create a plan to reach those goals. A plan includes specific steps that you’ll take to get there. For example, if you want to increase sales, you might write down five things you could do to increase sales. Each step has a purpose. Some steps will lead you closer to your goal while others will move you further away from it.
The second P stands for production. This includes the processes of transforming the raw material or data to an outcome or a product. A company cannot succeed without following proper processes. Without them, there would be chaos. For example, if a company does not plan properly, then it could end up wasting resources. Also, if a company does something wrong during production, then it could cause problems. Therefore, it is very important to follow proper processes.
Packaging is the how the company delivers its product to the customer. This step is crucial due to its impact on customers’ impression and their decision to buy the product. Packagin adds a value to the product and defines its image.
Promotion is a set of policies that interact and integrate with each other through the so-called promotion mix, which includes a number of
activities, which are:
– Advertising.
– Personal selling.
– Sales promotion.
– Publishing.
– Public relations.
Pricing policy is intended to determine the appropriate price of a product in
accordance with the variables of supply and demand in the market, as well as the
ability of customers to purchase that product.
Post-sale service: it is as important as the production, as it may include setting up the product, maintenance, periodic service and even returns.
These factors’ quality should be well controlled and determined through strict standards.
Learn about marketing 8 Ps here: Fundamentals of Marketing and Promotion. – SKILLTECS and here: The 4 Ps and 8 Ps of Marketing – A Marketing Mix – YouTube
Business
The Top 5 NASA’s Artemis Project Management Tools to Help You Manage Projects
Project management tools can help you manage projects effectively by providing information on tasks, deadlines, resources, costs, and other aspects of a project. The NASA Artemis program is a multi-year effort to land humans on the moon and beyond.
#projectmanagement
#NASA
#ARTEMIS

Project management tools can help you manage projects effectively by providing information on tasks, deadlines, resources, costs, and other aspects of a project. The NASA Artemis program is a multi-year effort to land humans on the moon and beyond. Here are five project management tools that are used by NASA that made the Artemis program become reality while the whole world is witnessing the countdown to launch.
Gantt Chart:
A Gantt chart is a type of diagram used to show the progress of a project. It shows the start date, duration, and completion dates of each task.
The Gantt chart is one of the most popular project management tools used today. It shows the progress of a project from beginning to end. Each task has a date assigned to it, and each task is linked to the next task. You can use a Gantt chart to see what needs to be done before a deadline, and you can easily track the progress of a project.
Task List:
If you’re looking for an easy way to manage projects, consider using a task list. This tool allows you to organize tasks into categories and subcategories so you can easily see at a glance where you stand with respect to completing them.
The NASA Artemis project management tool provides a task list that includes everything from project goals to project milestones. You can use the task list to keep track of what needs to be done, who needs to do it, and when it needs to be completed.
Resource Planner – An online tool that helps you plan projects by tracking resources and costs:
Another tool that will help you manage projects more effectively is a resource planner. A resource planner is a tool that helps you track the resources needed to complete a project. It also helps you estimate the cost of those resources.
The Resource Planner is one such tool that provides project managers with a comprehensive resource planning solution. It allows users to create a project schedule, track progress, and monitor costs. Users can also use the Resource Planner to assign tasks to team members and keep track of who has completed what.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) – A method used to break down large projects into smaller chunks.
WBS is an effective planning technique because it allows you to identify the tasks required to complete a project. This makes it easier to plan for the work involved in completing the project.
The WBS is one such tool that helps you organize your work breakdown structure. It breaks down the project into manageable pieces, which makes it easier to plan and execute the project.
The WBS is one such tool that helps you organize your work breakdown structure. You can use it to break down a project into manageable pieces, which makes it easier to plan and execute each task.
Calendar:
A calendar helps you keep track of deadlines and other events. It also lets you see when something needs to happen. If you need to meet with someone at a certain time, make sure you add it to your calendar, so you won’t forget.
The calendar tool at NASA’s website provides a visual representation of the entire project timeline. You can see what tasks are due next, which ones are completed, and which ones are currently being worked on.
-

 Management Tools4 years ago
Management Tools4 years agoWhat is the Drill-Down technique?
-

 Management Tools4 years ago
Management Tools4 years agoAll you need to know about the Pareto principle and the 80/20 rule.
-

 Business3 years ago
Business3 years agoCommunication Rights & Responsibilities
-

 Business4 years ago
Business4 years agoHow to manage Unplanned and Sudden Tasks in 6 Steps like a Master?
-

 Business4 years ago
Business4 years agoE.P.I.C. Model is the new trend in training delivery.
-

 Business4 years ago
Business4 years agoWhat is Curriculum Development and how to implement it?
-

 Management Tools4 years ago
Management Tools4 years agoThe Appreciation Technique
-

 Business4 years ago
Business4 years agoWhat do you know about the 4Rs Marketing Mix?







Pingback: The Power of Digging Deeper: Unraveling Problems with Root Cause Analysis » SKILLTECS