Business
The Concept Of Self-Managed Work Teams and how to develop them?

“The biggest challenge is to achieve the dream, not only my dream and my vision but the dream and vision of the group in the mind of each individual, in order to reach one voice and one culture. Let us work in the spirit of one team, regardless of position, and to maintain our performance.”
– Dr. Edson Gedoy Bueno
Self-managed work teams (SMWT) are considered one of the contemporary initiatives that help to maximize participation and engagement in terms of productivity and quality in addition to cost reduction and resources saving.
The trend in the business field has increased during the nineties of the past century to rely on self-management work teams, as they are called by many different names, such as:
- Self-directed teams.
- Autonomous improvement teams.
- Shared leadership teams.
- Autonomous work groups.
Thus, all researchers and writers agree that the core concept of self-managed work teams can be defined as “A group of individuals fully responsible for accomplishing certain tasks, such as manufacturing a product or providing a service, and making the necessary decisions to complete them, such as defining tasks and methods of achievement, arranging and scheduling tasks, holding meetings between team members to solve work problems, as well as taking care of raising personal issues”.
Reasons to transform to self-managed work teams:
- The outdated concept of management, which allows one person to issue orders and supervise a large number of individuals carrying out his/her orders, which leads to low levels of commitment and lack of loyalty, which results to low quality, performance and customer dissatisfaction.
- The best organizations are those that direct their attention to the lower levels of employees and not only to the customers. The best way to achieve this is to form working groups that work as one unit and allow its members to take the initiative in solving problems and making decisions and sharing success and best practices with management.
- The tendency to reduce the volume of labor to reduce costs and reduce the degree of bureaucracy, by relying on self-management, which leads to the disappearance of supervision and middle management, in addition to effective decision-making, flexibility of communication, and strengthening the behavior of organizational citizenship.
- Attention to total quality management, enhancing customer care, and desire for continuous improvement in performance, which requires more dynamic and creative work systems. Thus, the solution lies in empowering employees through self-managed work teams.
- The increasing interest in teamwork and the desire to achieve employees’ loyalty to the organization and their sense of job satisfaction, self-realization and quality of work life.
Limitations of implementing self-managed work teams:
Collectivism:
This constraint refers to the degree of importance an individual gives to teamwork versus individual action. Individuals who have value for teamwork tend to value the good of the team more than the good of the individual and tend to say (we), while individuals who have a low level of group sense, are characterized by independence and care about their own interests thus constitute an obstacle to the success of self-managed work teams because they have lack of desire to work with others and do not like to take responsibility at work, and tend to say (I).
Power distance:
This value expresses the degree of commitment that the individual has to participate in decision-making or the degree of influence on the decision taken by the administration. Being away from authority Individuals tend to submit to orders and not express opinions because they are accustomed to the hierarchical organization style. Therefore, it is difficult to keep pace with the style of self-managed work teams.
Doing orientation:
This restriction expresses the extent to which individuals are keen to go towards implementing the goals and adopting a strong motivation towards work, and this depends to a large extent on the clarity of the goal on the one hand and the benefits that will accrue to individuals as a result of achieving the goal on the other hand, which creates motivation among Individuals to move towards achievement, however, in the event of ambiguity of goals and lack of clarity of the benefits that individuals will obtain from achieving the goals, individuals will not have the motivation and desire to work with the team, not even bear the slightest responsibility.
The degree of determinism:
Individuals who feel unable to change the course of things within their organizations even with a broad mandate to them believe in determinism and result in excessive satisfaction with current conditions and in case of failure tend to withdraw or justify and then stop trying to reach the goal claiming that this is their fate. Therefore, they will not be in line with the style of work teams and self-management. As for individuals who have a low degree of inevitability in their culture, they take challenging positions to complete the required work even with the least powers available to them, as they have confidence in their abilities to influence the existing conditions and bring about change in the organization in line with achieving goals.
Shifting to self-managed work teams:
It cannot be easily assumed that individuals who are accustomed to a work environment with restrictions, and specific procedures, can suddenly switch to a work environment that allows them to make decisions and take responsibility. But when the team leader becomes a coordinator and collaborator, it will start to make the team act as a decision-making entity. And when the leader becomes more skilled in developing the team’s decision-making capabilities, he can turn to other duties while the team undertakes to perform its responsibilities and approaches, with the accumulation of its experience, to self-management.
The following table shows the transition towards more self-management:
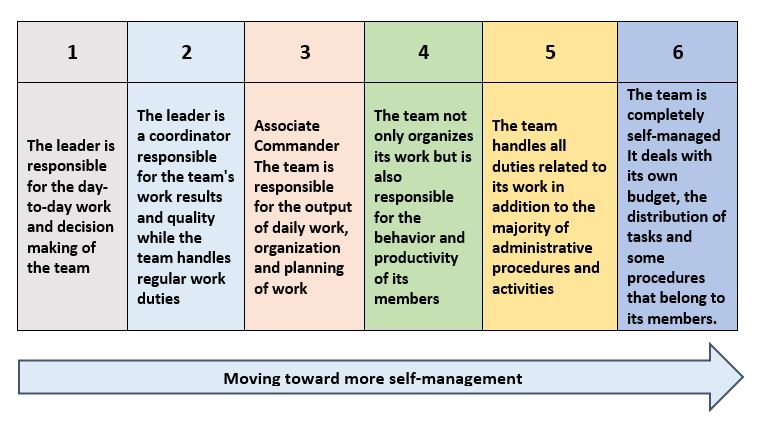
The optimum organizational structure for organizations to adopt self-managing work teams:
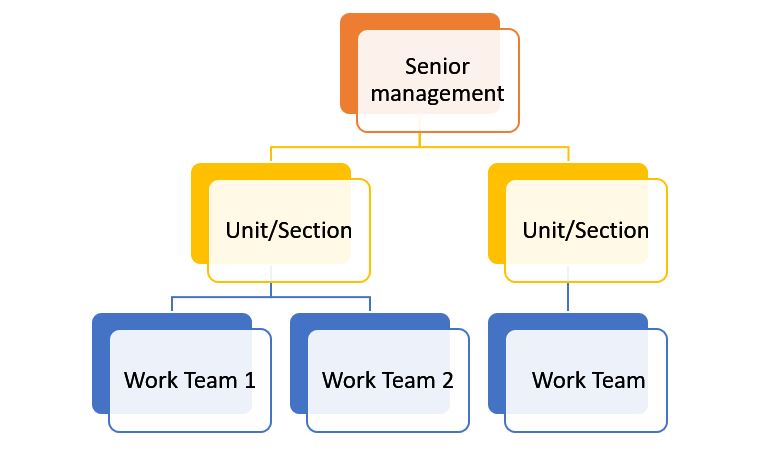
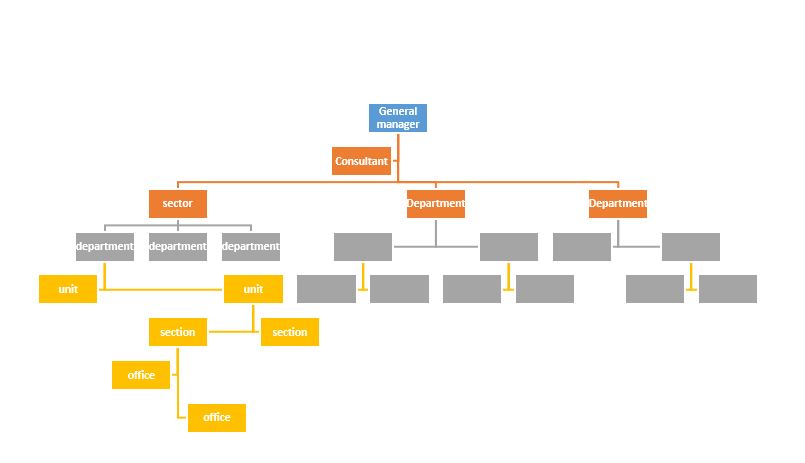
When there is a traditional structure with a broad hierarchy, and there are a number of different ranks, while some sectors are viewed with a different perspective that reduces their position in the organization; Working in the form of a responsible and self-managed work team is a very difficult process, and the activities of building these teams become very complex, so it was necessary to change the organizational structures in order to align with the work teams, as the organizational structure changed from a hierarchical form to a simple form that the middle management is limited and followed by the main sections, followed by work teams in the organization.
Organizational structure based on work teams:
Organizational structure based on hierarchy:
Responsibilities of self-managed work teams:
These teams bear a set of administrative and financial responsibilities that were limited to the senior management only, as these responsibilities and powers are transferred from outside the teams to within them in order to raise the level of performance, develop its quality and improve the quality of work life. This transformation is considered the most important characteristic of these self-managing teams.
- Job descriptions:
The job description process is considered one of the most bureaucratic processes carried out by the Human Resources Department, as each job is described accurately, the competencies required for it and the responsibilities assigned to it are determined, in addition to that, wages and salaries are determined accordingly, however, by applying the concept of self-managed work teams, fundamental changes occur to the job description process where it is expected and supposed that team members will be able to perform all the work and tasks assigned to the team. In addition to the exchange of skills and experiences that each individual can replace the other if necessary. Therefore, work is more flexible and ensures the provision of specialized and interchangeable human resources as a means to confront the dynamic nature of changing demand and the surrounding environment.
- Selection and appointment of new team members:
The logic of this responsibility is that the team is best able to know the actual needs of individuals, and not only financial and material needs, but also intangible needs, such as the degree of the individual’s dependence and devotion to teamwork and the ability to interact and deal with others in a harmonious and consistent manner within the teamwork in addition to the extent to which the individual’s personal values are consistent with the style of the self-managed team’s work.
It is important to modify the recruitment system to depend mainly on the work team, that is, the team members have the authority to appoint the new individual through:
- The team members manage the interviews that will be held with the candidates.
- The decision is made on the candidate’s ability and eligibility to be a member of the team.
- The team makes the decision to appoint the new member unanimously.
- Determining the financial needs:
Where the team determines the financial needs in order to carry out the tasks entrusted to it and achieve the goals, as these needs cover all the activities of the team in their various forms and diversity.
- Training and development:
Training needs are of paramount importance to the self-managed work team, where team members identify and assess needs and participate in designing appropriate training programs and evaluate training outcomes after implementation.
Thus, training should cover the following topics:
Self-management and leadership, where the team needs training in supervisory functions by learning how to carry out tasks, define performance standards, simplify work procedures, learn communication skills, conflict resolution, decision-making, meeting management, and time management.
In addition to responsibility for the work as a whole, team members need to learn the skills of dealing with customers, as well as dealing with suppliers, unions, banks….etc.
- Payroll and salary management:
The traditional system of salaries and wages is based on the job grade, as this system supports individual achievements only. Therefore, according to the concept of self-managing work teams, this system must be modified and replaced with a team-based system, and that the most used system in the payment of salaries and wages within work teams is the payment for knowledge, where wages are paid to team members based on the number and type of tasks that the team member can accomplish as well as the team’s participation in the gains and profits achieved depending on the team’s performance to motivate it to more effort and continuous improvement.
- Performance appraisal :
It relates to the responsibility of measuring the team’s performance level and efficiency. The team can achieve this responsibility through:
- Replacing the people’s appreciation with the team’s appreciation: this depends on the team’s responsibility, achieving its goals as a whole and not individually so that the team maintains the spirit of teamwork and is collectively rewarded.
- Self-evaluation: where the members evaluate their work and the team sets standards for all the tasks that are assigned to it, and each member knows what is required of him/her and can measure his/her performance on a constant periodic basis.
- Reports: they are prepared periodically to express the progress of the team in completing the work and submit it to the higher management.
Characteristics of self-managed work teams:
- It is a group of employees who develop relationships and have goals, roles, values and behavioral rules in addition to the desire to work, interact and work to reach the goal.
- Relying on open discussions as one of the democratic methods in making decisions.
- The team does not depend on senior management except in a small part, that is, it is relatively independent. It is self-moving and having a high degree of independence as it sets goals and plans, makes decisions, solves problems, allocates roles and assigns responsibility, monitors and evaluates.
- The results of the team’s work are the result of interaction, cooperation and harmony among the team members.
- The effectiveness of one team affects the effectiveness of other teams.
- The overall effectiveness of the organization consists of the effectiveness of the teams in it.
How to transform into self-managed work teams?
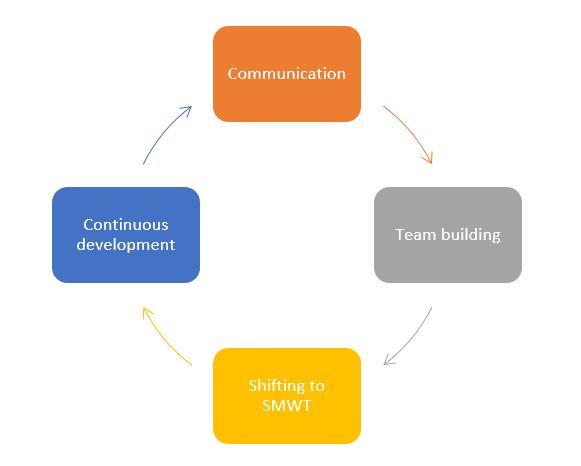
- Step 1: Communication:
This stage depends on the success of the communication process and the achievement of the desired commitment, in which the identity of the self-managed teams is defined, the extent to which it fits with the existing organizational culture, and clarification of the appropriate set of values and organizational vision for members.
- Step 2: Team building:
The time frame for this stage depends on the size of the organization and the culture of the workforce. Teams are being developed. The focus at this stage should be on the composition of the team, the tasks required of it, and the role of each member in it.
- Step3: Shifting to self-managed work teams:
At this stage, the process of transition and the development of self-managed work teams takes place and moves to work as an independent unit responsible for the product as a whole or the manufacturing process, where the administrative levels are reduced and often we find only two administrative levels linked by supportive units for work.
- Step4: Continuous development:
At this stage, the process of continuous improvement and development takes place internally, the process of transforming to self-managed teams all over the organization. In addition to integration with customers, Therefor, complete integration between the structures of the organization creates a competitive advantage for the organization.
Benefits achieved by successful self-managed work teams:
- Reducing costs.
- Improving the level of quality.
- Reducing the rates of loss and damage.
- Providing a high degree of flexibility within the work environment.
- Increasing the morale of the employees and reducing the rates of turnover.
Organizations applying self-managed work teams:
- GMC (for automotive industry).
- AMIL (a health care company).
- TOYOTA.
- General Electric.
Conclusion:
The commitment of the individual and his/her involvement in the work is are core values that lead to the development of the organization, and the organizations that promote those core values create a consensus between the needs of the individuals and the business needs, and this consensus often leads to the existence of an effective organization and individuals who are satisfied and enthusiastic in their work and have a sense of ownership. Therefore, a self-managed work team is an effective tool to achieve commitment and satisfaction along with growth and quality. However, that can happen through the learning and empowerment of the team.
Business
Cultural Constraints and Leadership: Navigating the Fine Line

Leadership is a challenge that requires a delicate balance of skills, adaptability, and emotional intelligence. However, these qualities may manifest differently in different cultural contexts, making the task even more complex. In this article, we delve into the realm of cultural constraints and leadership, exploring how leaders can navigate the fine line between different cultural norms and expectations.
Cultures shape our values, beliefs, and behaviors, and these factors play a significant role in leadership dynamics. Understanding cultural constraints is essential for leaders who operate in diverse environments and want to leverage cultural nuances to their advantage.
By embracing cultural intelligence, leaders can foster stronger relationships, build trust, and bridge differences. This requires sensitivity, curiosity, and a willingness to challenge preconceptions. Leaders who can adapt their leadership style to fit cultural contexts will be able to motivate and inspire their team members effectively.
We will explore case studies from different industries and examine how leadership styles have adapted to cultural constraints. By understanding and utilizing these valuable insights, leaders can navigate the fine line between respecting cultural differences and maintaining effectiveness in their leadership roles.
Understanding cultural constraints in different organizational contexts
Cultures shape our values, beliefs, and behaviors, and these factors play a significant role in leadership dynamics. In order to effectively navigate cultural constraints, leaders must first understand the unique characteristics of the cultural context in which they operate.
Different organizational contexts may have varying degrees of formality, hierarchy, and communication styles. For example, in some cultures, such as Japan, there is a strong emphasis on respect for authority and the need to maintain harmony within the group. In contrast, other cultures, such as the United States, may value individualism and direct communication.
Leaders who are aware of these cultural nuances can adapt their leadership style accordingly. They can adjust their communication approach, decision-making processes, and management techniques to ensure that they are aligning with the cultural expectations of their team members.
The impact of cultural constraints on leadership effectiveness
Cultural constraints can have a significant impact on leadership effectiveness. When leaders fail to understand or respect cultural differences, they may inadvertently create barriers that hinder collaboration and productivity within their team.
For example, a leader who is accustomed to a hierarchical leadership style may struggle to engage team members from a culture that values egalitarianism. In this case, the leader’s authoritative approach may be perceived as overbearing or dismissive, leading to a breakdown in trust and cooperation.
On the other hand, leaders who are able to adapt their leadership style to fit cultural constraints can foster a more inclusive and supportive environment. By valuing and incorporating diverse perspectives, leaders can tap into the unique strengths and talents of each team member, resulting in increased innovation and performance.
Strategies for navigating cultural constraints in leadership
Navigating cultural constraints requires a multifaceted approach that combines self-awareness, empathy, and a willingness to learn and adapt. Here are some strategies that leaders can employ to successfully navigate cultural constraints:
1. Educate yourself:
Take the time to learn about the cultural norms, values, and communication styles of the individuals you work with. This will help you better understand their perspectives and adapt your leadership approach accordingly.
2. Build relationships:
Cultivate strong relationships with team members from different cultural backgrounds. This will help you gain insights into their unique experiences and perspectives, and foster a sense of trust and collaboration.
3. Practice active listening:
Actively listen to your team members and demonstrate empathy. This will help you understand their needs, concerns, and aspirations, and enable you to tailor your leadership style to meet their individual and cultural expectations.
4. Be flexible:
Recognize that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to leadership. Be willing to adapt your leadership style to accommodate different cultural constraints and preferences.
5. Continuously learn:
Cultivate a growth mindset and seek out opportunities to learn from different cultural contexts. This can involve attending cultural awareness training programs, reading books and articles on cross-cultural leadership, or engaging in open and honest conversations with individuals from different cultural backgrounds.
By implementing these strategies, leaders can develop the cultural intelligence necessary to navigate cultural constraints and lead effectively in diverse environments.
Developing cultural intelligence for effective leadership
Cultural intelligence refers to an individual’s ability to navigate and adapt to different cultural contexts. It is a key competency for leaders who operate in multicultural environments, as it enables them to bridge differences, build trust, and effectively manage teams from diverse backgrounds.
Developing cultural intelligence begins with self-awareness. Leaders must first understand their own cultural biases, assumptions, and values in order to effectively navigate cultural constraints. This involves reflecting on their own cultural upbringing and experiences, and recognizing how these factors may shape their leadership style and decision-making processes.
Once leaders have a strong sense of self-awareness, they can then focus on developing their cultural knowledge. This involves actively seeking out information about different cultural norms, values, and communication styles. Leaders can engage in cross-cultural training programs, read books and articles on cultural intelligence, and engage in meaningful conversations with individuals from different cultural backgrounds.
In addition to self-awareness and cultural knowledge, leaders must also develop their cultural skills. This involves honing their ability to adapt their leadership style to align with different cultural expectations. Leaders can practice active listening, observe and learn from local leaders in different cultural contexts, and seek feedback from team members to ensure that their leadership approach is effective and inclusive.
By continually developing their cultural intelligence, leaders can navigate cultural constraints with confidence, build strong and diverse teams, and drive organizational success.
Case studies: Successful leaders navigating cultural constraints
Examining case studies of successful leaders who have effectively navigated cultural constraints can provide valuable insights and inspiration for other leaders facing similar challenges. Let’s explore a few examples:
1. Satya Nadella, Microsoft:
Satya Nadella, the CEO of Microsoft, has been praised for his ability to bridge cultural differences and foster collaboration within the organization. When he took over as CEO, he recognized the need to transform Microsoft’s culture to be more inclusive and open to new ideas. Under his leadership, Microsoft has become a more agile and innovative company, with a strong focus on diversity and inclusion.
2. Indra Nooyi, PepsiCo:
Indra Nooyi, the former CEO of PepsiCo, is known for her inclusive leadership style that embraces cultural diversity. She recognized the importance of understanding different cultural perspectives and incorporated them into PepsiCo’s strategies and decision-making processes. As a result, PepsiCo has been able to successfully navigate cultural constraints and expand its global footprint.
3. Carlos Ghosn, Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance:
Carlos Ghosn, the former CEO of the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance, is a well-known example of a leader who successfully navigated cultural constraints. He led a multinational organization with diverse cultural backgrounds, and he was able to bridge these differences by fostering a culture of respect, collaboration, and shared goals.
These case studies highlight the importance of cultural intelligence and adaptive leadership in navigating cultural constraints. By understanding and leveraging cultural differences, leaders can create inclusive and high-performing teams.
The role of diversity and inclusion in overcoming cultural constraints
Diversity and inclusion play a crucial role in overcoming cultural constraints and fostering effective leadership. Organizations that prioritize diversity and inclusion are better equipped to navigate cultural differences and leverage the unique perspectives and talents of their team members.
When leaders create an inclusive environment where individuals feel valued and respected, team members are more likely to share their diverse perspectives and ideas. This leads to increased innovation, problem-solving, and creativity within the organization.
Furthermore, diversity and inclusion initiatives can help leaders develop cultural intelligence and bridge cultural differences. By actively seeking out diverse perspectives and experiences, leaders can broaden their understanding of different cultural contexts and adapt their leadership style accordingly.
In order to promote diversity and inclusion, leaders can implement strategies such as:
– Diverse hiring practices:
Actively recruit individuals from different cultural backgrounds and ensure that selection processes are fair and unbiased.
– Inclusive communication:
Foster open and transparent communication channels that encourage all team members to contribute and share their perspectives.
– Training and development programs:
Offer cultural awareness and sensitivity training programs to help leaders and team members develop the skills necessary to navigate cultural constraints.
By prioritizing diversity and inclusion, leaders can create a culture that values and celebrates differences, enabling them to effectively navigate cultural constraints and drive organizational success.
Training and development programs for leaders in multicultural environments
To equip leaders with the skills necessary to navigate cultural constraints, organizations can implement training and development programs that focus on cultural intelligence and adaptive leadership.
These programs can include:
1. Cultural awareness training:
Provide leaders with an understanding of different cultural norms, values, and communication styles. This can involve workshops, seminars, or online modules that help leaders develop a deeper appreciation for cultural diversity.
2. Cross-cultural communication skills:
Offer training on effective cross-cultural communication techniques. This can help leaders navigate linguistic and cultural barriers, and ensure that their messages are understood and appreciated by team members from different cultural backgrounds.
3. Coaching and mentoring:
Pair leaders with mentors or coaches who have experience working in multicultural environments. This can provide leaders with valuable insights and guidance on how to navigate cultural constraints and develop their cultural intelligence.
4. Experiential learning opportunities:
Provide leaders with opportunities to immerse themselves in different cultural contexts. This can involve international assignments, job rotations, or cross-cultural team projects that enable leaders to gain firsthand experience and develop their cultural adaptability.
By investing in training and development programs, organizations can empower leaders to navigate cultural constraints with confidence and drive success in multicultural environments.
Overcoming common challenges in navigating cultural constraints
Navigating cultural constraints is not without its challenges. Leaders may encounter various obstacles along the way, such as:
1. Language barriers:
Communication can be hindered by differences in language proficiency. Leaders must find ways to bridge the language gap, such as using interpreters or providing language training for team members.
2. Preconceived stereotypes:
Leaders must actively challenge preconceived stereotypes and biases to foster an inclusive and respectful environment. This requires ongoing self-reflection and a commitment to learning and growth.
3. Resistance to change:
Cultural constraints may lead to resistance to change, particularly when existing practices and norms are deeply ingrained. Leaders must effectively communicate the benefits and rationale behind proposed changes to gain buy-in from team members.
4. Misinterpretation of signals:
Cultural differences can result in misinterpretation of non-verbal cues and signals. Leaders must be mindful of these differences and seek clarification when needed to avoid misunderstandings.
By acknowledging and addressing these challenges, leaders can develop strategies to overcome them and navigate cultural constraints more effectively.
Conclusion: Embracing cultural constraints for leadership success
In today’s globalized world, cultural constraints are an integral part of leadership dynamics. Leaders who embrace cultural differences and adapt their leadership style accordingly can build stronger relationships, foster trust, and inspire their team members.
Understanding cultural constraints begins with self-awareness and a commitment to continuous learning. Leaders must educate themselves about different cultural norms, values, and communication styles to effectively navigate cultural differences.
By developing cultural intelligence, leaders can bridge cultural constraints, foster diversity and inclusion, and drive success in multicultural environments. Through training and development programs, organizations can equip leaders with the necessary skills to navigate cultural constraints and lead effectively.
By embracing cultural constraints, leaders can navigate the fine line between respecting cultural differences and maintaining effectiveness in their leadership roles. In doing so, they can unlock the full potential of their teams and achieve sustainable success in today’s diverse and interconnected world.
Business
Beyond Barriers: Embracing Cultural Diversity in Leadership
Cultural Diversity in Leadership

In today’s globalized world, cultural diversity is no longer just a buzzword; it is a necessity, especially in leadership roles. As companies expand their operations and reach new markets, leaders who can navigate the complexities of cultural differences are in high demand. Gone are the days when a one-size-fits-all approach to leadership was effective. Instead, organizations are looking for leaders who can embrace diversity and leverage it as a strength.
Embracing cultural diversity in leadership goes beyond just ticking a box for diversity quotas. It requires a genuine understanding and appreciation of different cultures, customs, and perspectives. Leaders who can embrace cultural diversity can create inclusive environments where individuals from different backgrounds feel valued and empowered to contribute their unique perspectives. This ultimately leads to better decision-making, innovation, and overall business performance.
However, embracing cultural diversity in leadership is not without its challenges. It requires a commitment to ongoing learning, unlearning biases, and fostering an open and inclusive culture. It also requires leaders to be adaptable and flexible in their leadership styles to accommodate diverse needs and expectations.
In this article, we will explore the importance of embracing cultural diversity in leadership and provide practical tips for leaders to effectively navigate and leverage this diversity for organizational success.
Understanding Cultural Diversity – Definition and Importance
Cultural diversity refers to the presence of different cultures and cultural groups within a society, organization, or team. It encompasses differences in race, ethnicity, nationality, language, religion, customs, and traditions. Embracing cultural diversity in leadership is not just about token representation or meeting diversity quotas; it involves understanding and appreciating the unique perspectives, experiences, and values that individuals from different cultures bring to the table.
The importance of embracing cultural diversity in leadership cannot be overstated. Firstly, it fosters creativity and innovation. When people with different backgrounds come together, they bring a wide range of ideas, knowledge, and problem-solving approaches. This diversity of thought can lead to breakthroughs and new perspectives that can drive innovation within an organization.
Secondly, embracing cultural diversity in leadership enhances decision-making. When leaders consider different viewpoints and perspectives, they are more likely to make informed and well-rounded decisions. This can help avoid groupthink and promote critical thinking, leading to better outcomes for the organization.
Lastly, embracing cultural diversity in leadership improves employee engagement and retention. When individuals from diverse backgrounds feel valued and included, they are more likely to be engaged and committed to their work. This not only boosts productivity but also reduces turnover, saving organizations time and resources in recruiting and training new employees.
Benefits of Embracing Cultural Diversity in Leadership
Embracing cultural diversity in leadership brings numerous benefits to organizations. Firstly, it enhances problem-solving capabilities. When leaders embrace cultural diversity, they tap into a wealth of diverse perspectives, experiences, and knowledge. This allows them to approach problems and challenges from different angles, leading to more effective and innovative solutions.
Secondly, embracing cultural diversity in leadership fosters creativity and innovation. When individuals from different cultures come together, they bring unique ideas, insights, and approaches to the table. This diversity of thought can spark creativity, leading to the generation of new ideas and the ability to adapt to changing market demands.
Furthermore, embracing cultural diversity in leadership enhances cultural competency. Leaders who are culturally competent can navigate and bridge cultural differences effectively. They can understand and appreciate different customs, traditions, communication styles, and values, which is crucial when operating in diverse markets or managing multicultural teams.
Lastly, embracing cultural diversity in leadership improves employee morale and engagement. When individuals from different backgrounds feel included and valued, they are more likely to be motivated, engaged, and committed to their work. This positive work environment fosters collaboration, teamwork, and a sense of belonging, ultimately leading to higher productivity and employee satisfaction.
Challenges in Embracing Cultural Diversity in Leadership
While embracing cultural diversity in leadership brings significant benefits, it is not without its challenges. One of the main challenges is overcoming unconscious biases. We all have biases, whether conscious or unconscious, which can influence our perceptions, judgments, and decisions. These biases can hinder leaders from fully embracing and leveraging the potential of cultural diversity.
Another challenge is the potential for miscommunication and misunderstandings. Cultural differences can lead to different communication styles, non-verbal cues, and interpretations of behavior. Leaders must be mindful of these differences to ensure effective communication and avoid misunderstandings that can hinder collaboration and teamwork.
Additionally, managing diverse teams requires adaptability and flexibility in leadership styles. Different cultures may have different expectations of leadership, such as hierarchical versus collaborative leadership styles. Leaders must be able to adapt their approach to accommodate these diverse needs and expectations.
Strategies for Embracing Cultural Diversity in Leadership
To effectively embrace cultural diversity in leadership, leaders can adopt several strategies. Firstly, leaders should invest in their own cultural competence through education, training, and self-reflection. This involves developing an understanding of different cultures, customs, and traditions, as well as examining and challenging their own biases and assumptions.
Secondly, leaders should foster an inclusive culture that values and celebrates diversity. This can be done through promoting open dialogue, providing opportunities for cross-cultural interactions, and creating a safe and respectful environment where individuals feel comfortable expressing their unique perspectives.
Furthermore, leaders can encourage diversity in decision-making processes by seeking input from individuals with different backgrounds and perspectives. This can help avoid the pitfalls of groupthink and promote critical thinking.
Additionally, leaders should prioritize diversity and inclusion in talent acquisition and development. By actively seeking out diverse candidates and providing opportunities for their growth and development, organizations can build a culturally diverse leadership pipeline.
Building a Culturally Diverse Leadership Team
Building a culturally diverse leadership team requires a deliberate and strategic approach. Firstly, organizations should establish diversity and inclusion goals and integrate them into their leadership development programs. This can include mentorship and sponsorship programs specifically designed to support individuals from underrepresented backgrounds.
Secondly, organizations should invest in diversity training and education for both current and aspiring leaders. This training should focus on developing cultural competence, building inclusive leadership skills, and addressing unconscious biases.
Furthermore, organizations can implement diversity initiatives such as affinity groups or employee resource groups that provide a platform for individuals from similar cultural backgrounds to connect, share experiences, and advocate for their needs.
Lastly, organizations should actively seek out and nurture diverse talent through targeted recruitment strategies, partnerships with diverse organizations, and creating an inclusive hiring process that reduces bias.
Training and Development for Culturally Diverse Leaders
Training and development play a crucial role in supporting culturally diverse leaders. Organizations should provide opportunities for leaders to enhance their cultural competence through workshops, seminars, and immersive experiences. This can include cultural immersion programs, cross-cultural communication training, and cultural sensitivity workshops.
Additionally, organizations can offer leadership development programs specifically designed for culturally diverse leaders. These programs should focus on building inclusive leadership skills, addressing challenges specific to diverse leaders, and providing networking and mentorship opportunities.
Organizations should also create opportunities for diverse leaders to showcase their skills and expertise through speaking engagements, panel discussions, and industry events. This not only helps raise their profile but also provides them with valuable exposure and networking opportunities.
Case Studies – Companies that Embrace Cultural Diversity in Leadership
Several companies have successfully embraced cultural diversity in leadership and reaped the benefits. One such company is Microsoft. The tech giant has made diversity and inclusion a priority, actively working to increase the representation of women and underrepresented minorities in leadership positions. Microsoft has implemented initiatives such as unconscious bias training, diverse hiring panels, and employee resource groups to foster a culture of inclusion and diversity.
Another example is Unilever, a multinational consumer goods company. Unilever has embraced cultural diversity by implementing a global diversity strategy that focuses on gender balance, cultural diversity, and inclusion. The company has set ambitious targets for increasing the representation of women and individuals from underrepresented backgrounds in leadership positions. Unilever also provides diversity training and mentoring programs to support the development of diverse leaders.
Measuring the Impact of Cultural Diversity in Leadership
Measuring the impact of cultural diversity in leadership is essential to understand its effectiveness and make data-driven decisions. Organizations can use several metrics to assess the impact of cultural diversity, such as employee engagement surveys, turnover rates, and diversity representation at different levels of leadership.
Additionally, organizations can track the impact of diversity on key business metrics, such as innovation, customer satisfaction, and financial performance. This can be done through analyzing data on product development, customer feedback, and financial indicators to identify any correlations between cultural diversity in leadership and positive outcomes.
Furthermore, organizations can conduct qualitative research, such as interviews and focus groups, to gather feedback and insights from employees about the impact of cultural diversity on their experiences and performance.
Conclusion – Embracing Cultural Diversity for Success
Embracing cultural diversity in leadership is no longer an option; it is a strategic imperative for organizations operating in today’s globalized and diverse world. By embracing cultural diversity, leaders can tap into a wealth of diverse perspectives, experiences, and knowledge that can drive innovation, enhance decision-making, and improve employee engagement.
However, embracing cultural diversity in leadership requires a commitment to ongoing learning, unlearning biases, and fostering an inclusive culture. It also requires leaders to be adaptable and flexible in their leadership styles to accommodate diverse needs and expectations.
By implementing strategies such as investing in cultural competence, fostering an inclusive culture, and building a culturally diverse leadership team, organizations can successfully navigate and leverage cultural diversity for organizational success. Companies like Microsoft and Unilever have demonstrated the positive impact of embracing cultural diversity in leadership, paving the way for others to follow suit.
In conclusion, embracing cultural diversity in leadership goes beyond just ticking a box; it is about creating inclusive environments where individuals from different backgrounds feel valued and empowered to contribute their unique perspectives. By doing so, organizations can unlock the full potential of cultural diversity and thrive in today’s global marketplace.
Basics
The Power of Digging Deeper: Unraveling Problems with Root Cause Analysis

In today’s fast-paced world, it’s easy to fall into the trap of providing quick-fix solutions to problems without truly understanding their underlying causes. But what if I told you there’s a powerful tool that can help you cut through the surface-level issues and get to the root of the problem?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach that enables you to dig deeper and unravel the complex web of factors that contribute to a problem. By identifying the underlying causes, RCA empowers you to implement targeted and effective solutions that address the root of the issue, rather than just treating the symptoms.
Whether you’re a business owner looking to eliminate recurring problems or an individual striving for personal growth, mastering the art of RCA can be a game-changer.
In this article, we will explore the power of digging deeper through Root Cause Analysis and how it can transform the way you approach and solve problems. Get ready to unlock the secrets to lasting solutions and uncover the true power of RCA.
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a structured method used to identify the underlying causes of problems or incidents. It involves a comprehensive investigation into the factors that contributed to the issue, aiming to uncover the root cause rather than simply addressing the symptoms. By understanding the root cause, you gain valuable insights that enable you to implement effective solutions and prevent the problem from recurring.
RCA is commonly used in various fields, including business, engineering, healthcare, and quality management. It helps organizations and individuals examine their processes, systems, and behaviors to identify areas for improvement. By adopting a systematic and analytical approach, RCA provides a solid foundation for problem-solving and decision-making.
The Importance of Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis is essential for effective problem-solving and decision-making. It goes beyond surface-level solutions and helps you understand the underlying factors that contribute to a problem. By addressing the root cause, you can prevent the problem from recurring, saving time, resources, and frustration.
One of the key benefits of RCA is its ability to eliminate guesswork. It provides a structured framework that guides your investigation, ensuring that you consider all relevant factors and collect the necessary data. This systematic approach helps you avoid jumping to conclusions or implementing ineffective solutions.
RCA also encourages a proactive mindset. Instead of treating problems as isolated incidents, it encourages you to view them as opportunities for improvement. By focusing on the root cause, you can identify patterns, trends, and systemic issues that may be impacting your organization or personal life. This proactive approach allows you to address the underlying causes and create lasting solutions.
Benefits of Using Root Cause Analysis
Using Root Cause Analysis offers several benefits for both individuals and organizations. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
1. Effective Problem Solving:
RCA enables you to identify the root cause of a problem, allowing you to implement targeted and effective solutions. By addressing the underlying factors, you can eliminate the problem at its source, rather than just treating the symptoms.
2. Prevention of Recurring Issues:
By understanding the root cause, you can implement preventive measures that eliminate the likelihood of the problem recurring. This saves time, resources, and frustration in the long run.
3. Improved Decision Making:
RCA provides valuable insights that inform your decision-making process. By understanding the underlying causes, you can make more informed choices that align with your goals and objectives.
4. Enhanced Efficiency:
By addressing the root cause, you can streamline your processes and systems, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
5. Continuous Improvement:
RCA encourages a proactive approach to problem-solving, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. By consistently analyzing and addressing root causes, you can drive ongoing growth and development.
Steps to Conduct a Root Cause Analysis
Conducting a Root Cause Analysis involves a systematic approach that consists of several steps. While the specific steps may vary depending on the context and problem at hand, the following framework provides a general guideline:
1. Define the Problem:
Clearly articulate the problem or incident that you want to analyze. This step ensures that everyone involved has a shared understanding of the issue.
2. Gather Information:
Collect relevant data and information related to the problem. This may include incident reports, interviews, data analysis, and documentation. The goal is to gather as much information as possible to inform your analysis.
3. Identify Possible Causes:
Brainstorm and list all the potential causes that could have contributed to the problem. This step encourages creative thinking and ensures that you consider a wide range of possibilities.
4. Analyze Causes:
Evaluate each potential cause and determine its likelihood and impact. Use tools such as cause-and-effect diagrams, fishbone diagrams, or the 5 Whys technique to explore the relationships between causes and effects.
5. Determine the Root Cause:
Based on your analysis, identify the underlying factor or factors that are most likely responsible for the problem. This may involve further investigation and validation.
6. Develop Solutions:
Once you have identified the root cause, brainstorm and develop targeted solutions that address the underlying factors. Ensure that your solutions are practical, feasible, and aligned with your goals.
7. Implement and Monitor:
Put your solutions into action and monitor their effectiveness. This step allows you to assess whether the problem has been resolved and identify any potential issues or barriers.
8. Learn and Improve:
Reflect on the RCA process and outcomes. Identify lessons learned and areas for improvement to enhance your future problem-solving efforts.
By following these steps, you can conduct a thorough and effective Root Cause Analysis that uncovers the underlying causes of a problem and guides your decision-making process.
Tools and Techniques for Root Cause Analysis
There are various tools and techniques that can enhance your Root Cause Analysis process. Here are some commonly used ones:
1. Cause-and-Effect Diagrams:
Also known as Ishikawa or fishbone diagrams, these visual tools help you identify potential causes and explore their relationships. They provide a structured framework for brainstorming and categorizing causes into different categories, such as people, processes, equipment, environment, and materials.
2. 5 Whys Technique:
This technique involves repeatedly asking “Why?” to uncover the underlying causes of a problem. By digging deeper with each “Why?” question, you can reach the root cause.
3. Pareto Analysis:
This technique helps you prioritize the causes based on their frequency or impact. It allows you to focus on the most significant factors and allocate resources accordingly.
4. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA):
FMEA is a systematic approach used to identify potential failure modes and their effects. It helps you anticipate and prevent problems before they occur.
5. Statistical Analysis:
Statistical tools, such as regression analysis or hypothesis testing, can be used to analyze data and identify patterns or correlations that contribute to the problem.
These tools and techniques provide valuable frameworks and methodologies for conducting a thorough Root Cause Analysis. By leveraging them effectively, you can enhance your problem-solving capabilities and uncover deeper insights.
Common Challenges in Root Cause Analysis
While Root Cause Analysis offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that you may encounter during the process. Being aware of these challenges can help you navigate them effectively. Some common challenges include:
1. Complexity:
Some problems may have multiple causes and factors that interact in complex ways. Untangling this complexity requires patience, thoroughness, and a systematic approach.
2. Limited Data or Information:
Insufficient or incomplete data can hinder your analysis and make it challenging to identify the root cause. In such cases, it may be necessary to gather additional information or use alternative analytical methods.
3. Subjectivity:
Root Cause Analysis involves interpretation and judgment, which can introduce subjectivity. It’s crucial to ensure that your analysis is based on objective data and evidence, minimizing bias.
4. Time Constraints:
Conducting a thorough RCA takes time, and tight deadlines may limit your ability to explore all potential causes. In such situations, it’s important to prioritize and focus on the most significant factors.
5. Resistance to Change:
Implementing solutions based on the root cause may require changes to processes, systems, or behaviors. Resistance to change can pose challenges and require effective change management strategies.
By recognizing and addressing these challenges, you can navigate the Root Cause Analysis process more effectively and achieve more accurate results.
Real-Life Examples of Successful Root Cause Analysis
To illustrate the power of Root Cause Analysis, let’s explore some real-life examples where RCA has been successfully applied:
1. Manufacturing Industry:
A manufacturing company experienced frequent product defects, resulting in increased costs and customer complaints. By conducting an RCA, they discovered that a faulty machine component was causing the defects. They implemented a targeted solution, replacing the faulty component and improving quality control processes, resulting in a significant reduction in defects.
2. Healthcare:
A hospital noticed a high rate of patient falls and injuries. Through RCA, they identified insufficient staff training, poorly designed rooms, and inadequate patient monitoring as contributing factors. By addressing these root causes, they implemented training programs, redesigned rooms to improve patient safety, and enhanced monitoring protocols, resulting in a decrease in falls and injuries.
3. Software Development:
A software development team faced recurring software bugs and delays. RCA revealed that miscommunication and unclear requirements were causing the issues. By improving communication channels, implementing a more structured requirements gathering process, and enhancing quality assurance practices, they were able to deliver software with fewer bugs and on schedule.
These examples demonstrate the transformative impact of Root Cause Analysis. By digging deeper and uncovering the underlying causes, organizations can implement targeted solutions that address the root of the problem, resulting in improved outcomes and increased efficiency.
Implementing Solutions Based on Root Cause Analysis
Identifying the root cause is only the first step. To achieve lasting solutions, it’s crucial to implement the recommendations effectively. Here are some key considerations when implementing solutions based on Root Cause Analysis:
1. Clear Communication:
Clearly communicate the identified root cause, recommended solutions, and the rationale behind them. Ensure that all stakeholders understand the importance of addressing the root cause and the benefits of the proposed solutions.
2. Engage Relevant Stakeholders:
Involve all relevant stakeholders in the implementation process. This may include employees, management, customers, or other external partners. Engaging stakeholders fosters ownership, collaboration, and commitment to the solutions.
3. Allocate Resources:
Provide the necessary resources, such as funding, time, and expertise, to implement the solutions effectively. Consider the potential costs and benefits of the solutions and allocate resources accordingly.
4. Monitor and Evaluate:
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of the implemented solutions. Collect data, measure outcomes, and assess whether the root cause has been effectively addressed. This allows you to make necessary adjustments and ensure long-term success.
5. Promote a Learning Culture:
Encourage a learning culture within your organization or personal life. Embrace the lessons learned from Root Cause Analysis and use them to drive continuous improvement. Foster a mindset of curiosity, innovation, and adaptability.
By implementing solutions based on Root Cause Analysis effectively, you can create lasting change and improve your problem-solving capabilities.
Training and Resources for Mastering Root Cause Analysis
Mastering Root Cause Analysis requires knowledge, skills, and experience. Fortunately, there are various training programs, resources, and tools available to help you enhance your RCA capabilities. Here are some options to consider:
1. Training Programs:
Enroll in RCA training programs or workshops offered by professional organizations, universities, or consulting firms. These programs provide in-depth knowledge, practical techniques, and case studies to develop your RCA skills.
2. Certifications:
Pursue certifications in Root Cause Analysis, such as the Certified RCA Analyst (CRAA) or the Certified RCA Facilitator (CRAF). These certifications validate your expertise and enhance your professional credibility.
3. Books and Publications:
Explore books, articles, and publications on Root Cause Analysis. Authors like Ishikawa, Deming, or Ohno have made significant contributions to the field and offer valuable insights.
4. Online Resources:
Leverage online platforms, forums, and communities dedicated to Root Cause Analysis. Engage in discussions, ask questions, and share experiences to learn from others in the field.
5. Internal Training and Mentoring:
If you’re part of an organization, seek internal training or mentoring opportunities. Learn from experienced colleagues or experts within your organization who have expertise in RCA.
By investing in your RCA skills and leveraging the available resources, you can become a proficient Root Cause Analyst and drive meaningful change in your personal and professional life.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Root Cause Analysis
In our fast-paced world, taking the time to dig deeper and understand the root causes of problems is crucial for lasting solutions. Root Cause Analysis provides a systematic and structured approach to unraveling complex issues, empowering you to address the underlying causes rather than just treating the symptoms. By mastering the art of RCA, you can transform the way you approach and solve problems, whether in your business or personal life.
Root Cause Analysis offers numerous benefits, including effective problem-solving, prevention of recurring issues, improved decision-making, enhanced efficiency, and a culture of continuous improvement. By following a systematic process and leveraging tools and techniques, you can conduct a thorough RCA and uncover deeper insights.
While Root Cause Analysis presents challenges, such as complexity, limited data, subjectivity, time constraints, and resistance to change, recognizing and addressing these challenges can help you navigate the process effectively.
Real-life examples demonstrate the power of RCA in various industries, from manufacturing to healthcare to software development. Implementing solutions based on RCA requires clear communication, stakeholder engagement, resource allocation, monitoring, and a learning culture.
To master Root Cause Analysis, explore training programs, certifications, books, online resources, and internal mentoring opportunities. By investing in your RCA skills, you can become a proficient problem-solver and drive meaningful change.
Harness the power of Root Cause Analysis and unlock the secrets to lasting solutions. Dig deeper, understand the root causes, and transform the way you approach and solve problems. Get ready to unravel complex issues and unleash the true power of RCA.
-

 Management Tools4 years ago
Management Tools4 years agoWhat is the Drill-Down technique?
-

 Management Tools4 years ago
Management Tools4 years agoAll you need to know about the Pareto principle and the 80/20 rule.
-

 Business3 years ago
Business3 years agoCommunication Rights & Responsibilities
-

 Business4 years ago
Business4 years agoHow to manage Unplanned and Sudden Tasks in 6 Steps like a Master?
-

 Business4 years ago
Business4 years agoE.P.I.C. Model is the new trend in training delivery.
-

 Business4 years ago
Business4 years agoWhat is Curriculum Development and how to implement it?
-

 Management Tools4 years ago
Management Tools4 years agoThe Appreciation Technique
-

 Business4 years ago
Business4 years agoWhat do you know about the 4Rs Marketing Mix?





Pingback: https://canadianpharmaceuticalsonline.home.blog/
Dr. Mahmoud Elhalabi
September 4, 2022 at 10:46 am
It is my pleasure 🙂 stay tuned for more related articles 🙂